ADVERTISEMENT
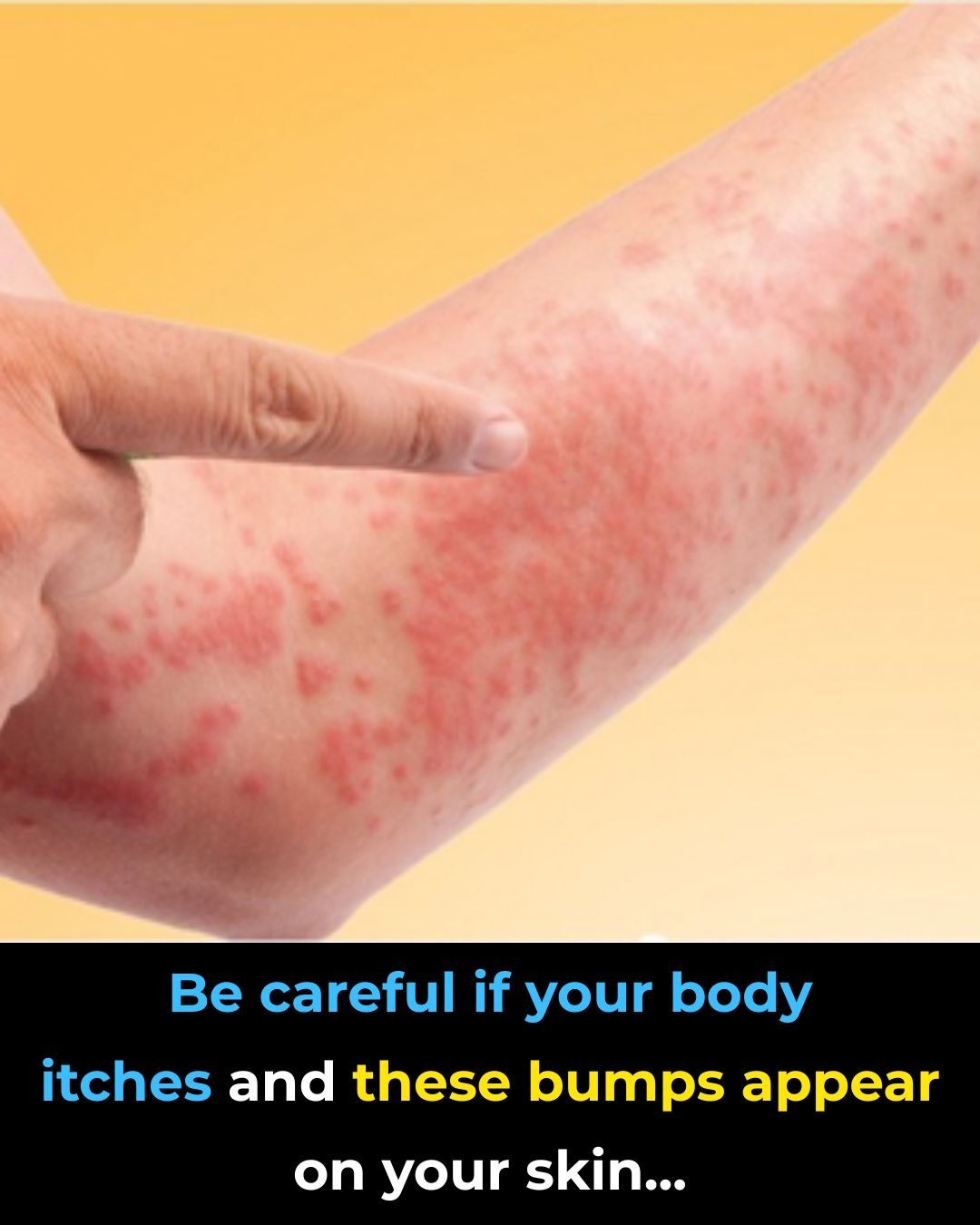
1. Stress and Anxiety
Emotional stress can actually trigger hives in some people. Stress increases the release of certain chemicals in the body, like histamine, which can cause inflammation and itchy welts. Even chronic low-level stress may lead to repeated outbreaks, making stress management techniques — like meditation, exercise, or deep breathing — an important part of prevention.
2. Temperature Changes
Cold air, hot showers, or sudden temperature swings can provoke hives. Some people develop cold-induced urticaria, where exposure to chilly temperatures causes itching and swelling. Conversely, heat or sweating can trigger cholinergic urticaria, a type of hives that appears after exercise or exposure to high temperatures.
3. Infections
4. Certain Foods and Additives
While allergies to foods like shellfish, peanuts, or eggs are well-known triggers, even non-allergenic ingredients such as food additives, preservatives, or artificial colors can cause hives in sensitive individuals. Common culprits include sulfites, benzoates, and certain dyes in processed foods.
5. Medications
Prescription and over-the-counter medications may also trigger hives. Antibiotics like penicillin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, and even some pain relievers can provoke a reaction in susceptible individuals. If you notice hives after starting a new medication, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
6. Physical Triggers
Certain physical actions can induce hives in a phenomenon called physical urticaria. Scratching, rubbing, pressure on the skin, or exposure to sunlight (solar urticaria) are potential triggers. Awareness of these triggers can help you adjust your daily habits and reduce outbreaks.
7. Underlying Medical Conditions
Sometimes, hives can signal an underlying autoimmune disorder, thyroid disease, or other chronic illness. If hives persist for weeks, occur frequently, or are accompanied by other symptoms like swelling, difficulty breathing, or fever, it’s important to seek medical evaluation.
ADVERTISEMENT